AI Test Analyst vs. Traditional QA Roles
Compare AI Test Analysts and traditional QA: differences in tools, workflows, coverage, and how hybrid teams blend AI automation with human oversight.
AI Test Analyst vs. Traditional QA Roles
AI is transforming the way QA testing works. Instead of relying solely on manual processes, QA teams are integrating AI tools to automate repetitive tasks, improve test coverage, and reduce maintenance time. This evolution has introduced new roles like AI Test Analysts, who specialize in managing these tools, while traditional QA professionals continue to focus on manual scripting and exploratory testing.
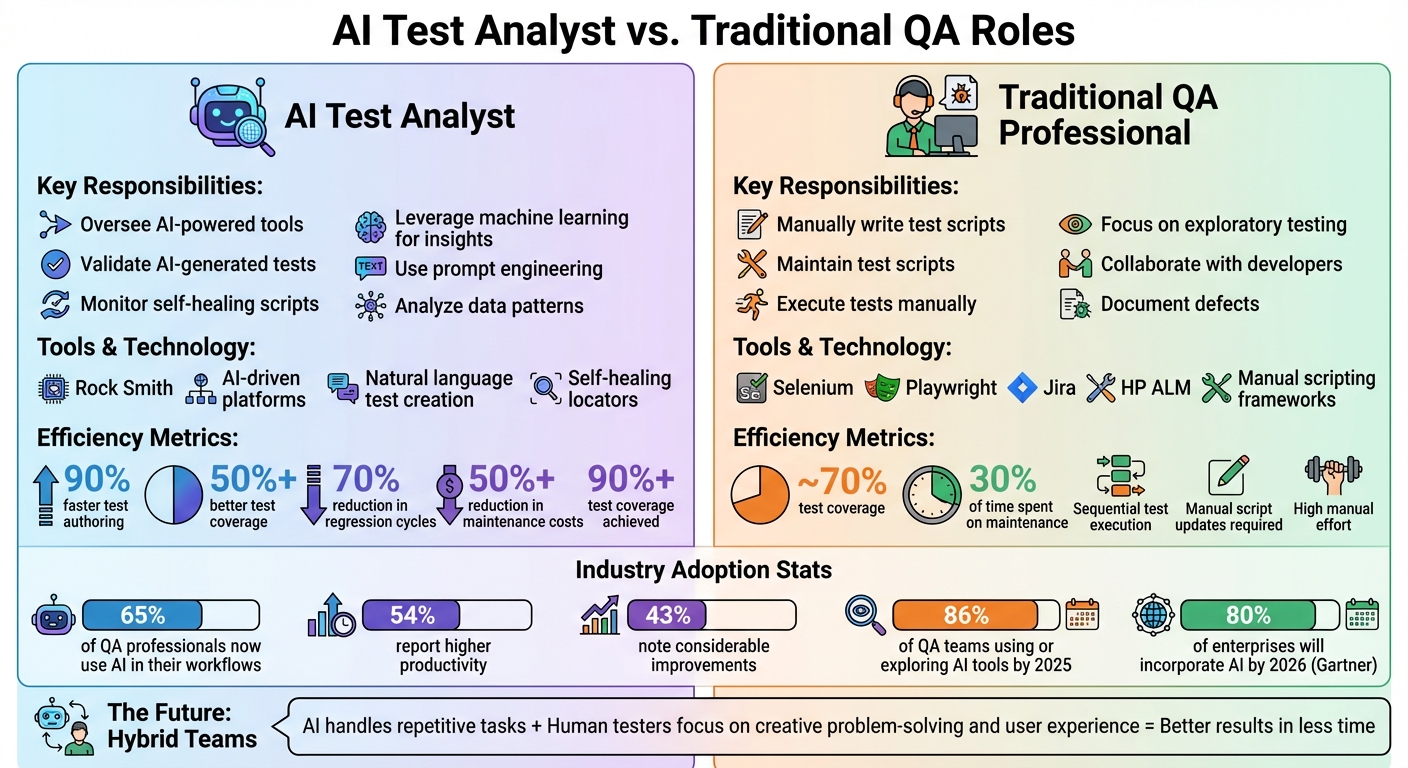
Here’s the key difference: AI Test Analysts use AI-driven platforms to auto-generate tests, monitor self-healing scripts, and analyze data for patterns. Traditional QA professionals, on the other hand, manually create and maintain scripts, which can be time-intensive. AI tools like Rock Smith can reduce regression cycles by up to 70% and cut maintenance costs by over 50%, but they require a shift in skills and mindset.
Quick Overview:
- AI Test Analysts: Oversee AI-powered tools, validate AI-generated tests, and leverage machine learning for insights.
- Traditional QA Professionals: Manually write and maintain test scripts, focus on exploratory testing, and collaborate with developers.
- Efficiency Gains with AI: Faster test creation, higher coverage (90%+), and reduced maintenance effort.
The future of QA lies in hybrid teams, where AI handles repetitive tasks and human testers focus on creative problem-solving and user experience. By combining AI tools with human expertise, QA teams can deliver better results in less time.
AI Test Analyst vs Traditional QA: Role Comparison and Key Differences
How AI is Transforming Software Testing Roles Forever
sbb-itb-eb865bc
Daily Tasks: What Each Role Does
Daily tasks highlight the clear differences in workflow and focus between AI Test Analysts and traditional QA professionals.
What AI Test Analysts Do
AI Test Analysts oversee intelligent systems instead of manually creating test scripts. Their day often starts with configuring AI-driven platforms like Rock Smith, which use AI agents to analyze applications visually and generate test flows in plain English. A key part of their job is refining these outputs through prompt engineering to ensure the AI produces effective and relevant tests.
Once the tests are generated, they validate them, making sure they cover edge cases and correctly identify high-risk areas. They also monitor self-healing mechanisms, which adapt to UI changes automatically, stepping in only when anomalies arise. Data analysis plays a big role in their responsibilities - they use machine learning models to detect patterns in test results, predict potential defect areas, and cluster flaky tests based on root causes, such as timing issues or selector drift.
For example, in 2025, Bloomberg engineers used AI heuristics to group and stabilize flaky tests, cutting regression cycle time by 70%. AI Test Analysts are also involved in monitoring real-time application behavior in production environments, catching issues that may slip through pre-release testing.
This role contrasts sharply with the manual, hands-on approach of traditional QA professionals.
What Traditional QA Professionals Do
Traditional QA professionals rely heavily on manual workflows. Their process begins with analyzing requirements and designing test cases to match. They write detailed scripts, often using frameworks like Selenium, specifying every step, locator, and assertion. Tests are then executed either manually or through pre-written automation suites, followed by a meticulous review of logs to pinpoint failures.
When UI changes occur, these professionals must manually update broken scripts, fix locators, and track new element IDs. They document defects in tracking tools and work closely with developers to reproduce issues. Exploratory testing is another key task, helping uncover problems that automated scripts might miss. While this approach benefits from human intuition, the repetitive nature of regression testing and constant script maintenance can slow down release cycles, especially in fast-paced CI/CD environments.
Responsibilities Comparison Table
Here’s a side-by-side look at the responsibilities of each role:
| Responsibility Category | AI Test Analyst | Traditional QA Professional |
|---|---|---|
| Test Creation | Validates AI-generated tests from requirements and specs | Designs and executes manual tests based on specifications |
| Test Execution | Manages autonomous agents with diff-aware prioritization to run relevant tests | Executes tests manually or runs static, hand-coded automation suites |
| Maintenance | Oversees self-healing locators and adaptive wait strategies | Updates scripts manually when UI or code changes break tests |
| Data Handling | Leverages AI to create synthetic, compliant datasets and analyze large data volumes | Prepares or masks test data manually for each scenario |
| Analysis | Utilizes machine learning to identify patterns, predict defects, and cluster flaky tests | Reviews logs and results manually to detect bugs and root causes |
| Defect Reporting | Analyzes AI-generated insights, production anomalies, and DORA metrics | Documents findings and reports defects manually to developers |
The shift toward AI is already making waves. Around 65% of QA professionals now incorporate AI into their processes, with 54% reporting higher productivity and 43% noting considerable improvements. Microsoft’s internal AI systems, for instance, identified 49,000 flaky tests, preventing nearly 160,000 false failures from disrupting delivery pipelines. Rather than replacing human testers, AI is lightening the load of repetitive tasks, allowing QA teams to focus on more strategic and high-impact testing activities.
Tools and Technologies: AI vs. Manual
The tools QA teams choose can dramatically influence their workflow, delivery speed, and time spent on maintenance. This section dives into how AI-driven tools stack up against traditional frameworks in terms of efficiency, upkeep, and impact on testing processes. These contrasts highlight the evolving roles of AI Test Analysts compared to traditional QA professionals. While traditional QA relies on manual scripting and constant maintenance, AI-powered platforms like Rock Smith take much of that load off through self-healing features and natural language capabilities.
AI Testing Tools
AI platforms like Rock Smith use intelligent agents to handle the entire testing lifecycle with minimal human input. These tools can "understand" applications visually, automatically create test flows in plain English, and execute tests in real-time using semantic targeting that adapts to UI changes. They also generate edge cases and simulate diverse user behaviors. Thanks to these capabilities, AI-driven tools can deliver up to 90% faster test authoring and 50% better test coverage compared to traditional methods. For example, a test suite with 1,000 cases that would take 10 hours to run manually can be completed in under an hour using autonomous AI tools.
AI's growing role is reflected in the fact that 54% of QA professionals now use ChatGPT for tasks like generating test cases and debugging, while 23% rely on GitHub Copilot. Additionally, AI tools offer predictive analytics to pinpoint high-risk areas even before testing begins.
Traditional QA Tools
On the other hand, traditional QA tools lean heavily on manual scripting. Frameworks like Selenium and Playwright, paired with tools like Jira and HP ALM, require testers to write detailed scripts. These scripts are prone to breaking with even minor UI changes, demanding constant updates. This leads to a significant maintenance burden that eats into team resources. Traditional tools also tend to run tests sequentially, which can unnecessarily execute the entire suite and slow feedback loops. While these tools are well-established and widely used, they lack the adaptability and intelligence AI tools bring to the table.
"Automation scripts are often brittle, and their maintenance can consume up to 30% of a team's time." - Software Testing Bureau
Tools Comparison Table
Here’s a quick look at how AI and traditional tools differ across key areas:
| Tool Type | AI Advantages | Traditional Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Test Creation | Auto-generates cases from PRDs or natural language; up to 90% faster | Requires manual scripting and advanced knowledge of tools like Selenium |
| Maintenance | Self-healing locators that adapt to UI changes automatically | Scripts break with minor UI changes, requiring manual fixes |
| Execution | Risk-based prioritization; runs only relevant tests per commit | Sequential execution slows down feedback loops |
| Defect Detection | Predictive analytics identify high-risk areas before problems arise | Bugs are often found reactively after a test fails |
| Setup & Skills | Low-code/no-code approach accessible to non-technical users | High manual effort; requires specialized SDET skills |
AI tools also bring cost efficiency into the mix. Running a full test suite with AI agents costs just $0.02–$0.05 per flow, while traditional setups rely on ongoing manual labor and upkeep. With 86% of QA teams either using or exploring AI tools by 2025, the trend toward intelligent, adaptive platforms is reshaping the testing landscape.
Workflows: Manual vs. Automated Processes
Let’s take a closer look at how workflows differ between traditional QA and AI-enhanced testing. These workflows highlight the contrast between manual processes and AI-driven methods. In traditional QA, manual interpretation dominates every step. On the other hand, AI-driven workflows introduce automation early, with AI agents generating test cases even before the sprint begins. These agents pull data from requirements, OpenAPI specifications, or live production traffic, streamlining the process significantly. This comparison sets the stage for understanding the day-to-day differences between these approaches.
How Traditional QA Works
Traditional QA is a step-by-step, labor-heavy process. Testers begin by manually reviewing requirements to identify what needs testing. Then, they create test cases manually, a time-consuming task. Execution follows, often involving running the entire regression suite, even if only a small part of the code has changed. If UI elements are updated, scripts often break, requiring testers to spend hours fixing locators manually. The analysis phase is equally tedious, involving a detailed review of raw pass/fail logs and identifying flaky tests. According to Google, about 1.5% of all test runs are flaky, and nearly 16% of tests exhibit some level of flakiness.
This sequential, manual approach contrasts sharply with the dynamic, automated methods AI Test Analysts rely on to speed up workflows.
How AI Test Analysts Work
AI Test Analysts leverage intelligent agents to automate and optimize the testing process. Tools like Rock Smith allow AI agents to visually interpret applications, auto-generate test flows in plain English, and prioritize tests based on changes in the code (also known as diff-aware prioritization). When UI elements are updated, self-healing locators detect and adjust to DOM changes automatically, cutting maintenance costs by more than 50%. Additionally, AI clusters failures by their root cause, distinguishing genuine bugs from environmental issues or flaky tests. This significantly accelerates diagnosis. In this approach, the tester’s role shifts to supervising AI outputs, fine-tuning parameters, and validating domain-specific logic.
"AI testing introduces mechanisms, not magic. From auto-generation of candidate cases to diff-aware prioritization, self-healing scripts, and flake clustering, AI augments QA where scripts break down." - Qadence
Workflow Comparison Table
| Workflow Stage | Traditional QA Process | AI Test Analyst Process | Efficiency Gains |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning & Analysis | Manual review of requirements | AI-driven discovery from specs, APIs, and traffic logs | Pre-sprint readiness with better edge case coverage |
| Test Creation | Manual scripting using IDs/XPaths; labor-intensive | Automated generation of test cases and scripts | 40–70% of regression candidates generated automatically |
| Execution | Manual or full-suite automated runs; often slow | Diff-aware prioritization; parallel execution in CI/CD | Regression cycles significantly shortened |
| Maintenance | Manual repair of broken scripts after UI changes | Self-healing locators | Over 50% reduction in maintenance costs |
| Reporting | Raw pass/fail logs; manual defect triaging | Predictive analytics and DORA-aligned dashboards | Faster root cause analysis and actionable insights |
This table underscores the efficiency gains at every stage of the workflow when using AI-driven approaches, from planning to reporting. By automating repetitive tasks and providing advanced analytics, AI transforms QA into a faster, more precise process.
Pros and Cons of Each Approach
Let’s break down the advantages and challenges of AI Test Analysts versus traditional QA roles. Each brings unique strengths to the table, but also faces its own hurdles. Understanding these differences can help teams fine-tune their testing strategies for better outcomes.
Benefits of AI Test Analysts
AI-driven testing offers a significant boost in speed and coverage. Test suites can run up to 10 times faster, with coverage jumping from around 70% to over 90%. Features like self-healing locators, which adapt to UI changes automatically, cut maintenance costs by more than 50%.
AI is also particularly skilled at uncovering edge cases that human testers might miss. By analyzing API schemas, traffic logs, and historical data, AI can generate scenarios such as malformed inputs or unexpected action combinations. A great example? Microsoft's internal AI system flagged 49,000 flaky tests, saving the company from dealing with approximately 160,000 false failures.
Another standout feature is AI’s ability to "shift left." It can generate tests early in the development cycle, even before a sprint begins, using user stories and API specifications. This early detection capability helps reduce the cost of software issues, which amounted to a staggering $2.41 trillion in losses for the U.S. market in 2022. Plus, nearly 43% of QA professionals report improved productivity and test coverage after adopting AI.
Challenges of Using AI
Despite its advantages, AI testing isn’t without its difficulties. For starters, 21% of QA professionals point to high licensing fees, infrastructure costs, and the need for specialized training as significant barriers. On top of that, the quality of data fed into the AI critically impacts its reliability.
Another concern is the "black box" nature of AI. This lack of transparency makes it hard to understand how certain conclusions are reached. In high-stakes fields like finance or healthcare, this can be a dealbreaker, as errors or "hallucinations" could lead to severe consequences. Research shows that AI-generated test cases are executable 70% to 90% of the time, depending on the complexity of the product. This highlights the importance of human oversight to ensure AI-generated tests align with real-world logic.
Data privacy and security concerns also pose challenges, with 34% of QA professionals listing this as a top issue when dealing with sensitive application data. Additionally, AI struggles to evaluate complex business logic or user experience nuances, areas where human intuition is indispensable.
As Hannah Son from TestRail aptly puts it:
"AI isn't replacing testers; it's helping some work more efficiently. But for most, the shift is still just beginning."
Strengths and Weaknesses Comparison Table
Here’s a quick side-by-side look at how traditional QA roles and AI Test Analysts stack up:
| Criterion | Traditional QA Roles | AI Test Analysts |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Limited by team size and manual effort. | Highly scalable; runs thousands of tests effortlessly. |
| Efficiency | Slower; manual execution and script updates take time. | Faster execution with minimal manual input. |
| Test Coverage | About 70%; prone to missing edge cases. | Over 90%; excels at generating edge cases. |
| Human Involvement | High; requires manual design, execution, and analysis. | Lower; focuses on setup, strategy, and monitoring. |
| Adaptability | Low; manual updates needed for changes. | High; self-healing locators adapt automatically. |
| Initial Cost | Lower; involves labor and basic tools. | Higher; requires investment in AI tools and infrastructure. |
| Business Logic & UX | Strong; human intuition handles complex workflows. | Limited; struggles with nuanced logic and user experience. |
| Reliability | Trusted but subject to human error. | Can produce false positives without oversight. |
Each approach has its place, and the best choice often depends on the specific needs and constraints of your project. Balancing human expertise with AI capabilities can often yield the best results.
The Future: Combining AI and Traditional QA
AI in QA: 2026 and Beyond
By 2026, Gartner predicts that 80% of enterprises will have incorporated AI into their delivery pipelines. The industry is leaning toward what’s known as the "Centaur Model", a collaboration between humans and machines. This model doesn’t aim to replace human testers but instead assigns AI the repetitive tasks like execution and maintenance, leaving humans to focus on strategic decisions and nuanced domain-specific judgments. A notable shift is happening - from prioritizing "100% code coverage" to concentrating on "risk coverage", which targets business-critical areas and high-impact user experiences.
One standout development is the emergence of autonomous agents. These AI systems can observe, reason, and act throughout the software stack. For example, they can propose tests based on code changes rather than relying on static scripts. They even replicate human browsing behavior to uncover practical issues, while predictive defect analysis uses historical data to highlight error-prone areas before testing begins.
This evolution is setting the stage for hybrid teams, blending the efficiency of AI with the insight and oversight of human testers.
How Hybrid QA Teams Work
In this hybrid approach, successful QA teams don’t choose between AI and humans - they combine the strengths of both. AI takes on tasks like running thousands of regression tests simultaneously and simulating large-scale user loads for performance testing. Meanwhile, human testers focus on reviewing flagged anomalies and conducting exploratory testing that requires creativity and intuition. This reflects a broader shift from manual testing to a more intelligent, collaborative process.
In this setup, AI handles repetitive regression tests, high-volume data analysis, and load testing. Humans, on the other hand, step in to make contextual decisions and ensure the overall quality of the product.
"The future of software testing is not about AI versus humans; instead, it's about AI working in conjunction with humans."
Traditional QA roles are evolving. Professionals now guide quality objectives and validate AI outputs, spending less time on repetitive tasks and more on high-value activities like exploratory testing and user advocacy. In fact, 34% of QA professionals report that AI has allowed them to focus on more complex and rewarding work.
Getting Ready for AI in QA
Adopting a hybrid QA model doesn’t require an overnight transformation. Start small by automating low-risk, repetitive tasks like smoke tests and regression suites, and gradually expand to more intricate scenarios. Tools like Rock Smith simplify this process by using AI agents to visually interpret applications and create test flows in plain English, reducing the need for advanced coding skills.
The skill set for QA professionals is also shifting. To stay ahead, it’s essential to build AI literacy, including skills in data analytics, basic machine learning, and understanding AI-generated reports. QA roles now emphasize investigation, interpretation, and intervention. Key capabilities include analyzing AI behavior, developing effective prompts, and acting as the "Human-in-the-Loop" to oversee critical decisions.
Establishing feedback loops is crucial. Human testers should regularly validate AI findings, fine-tune testing parameters, and adjust data strategies as needed. Hosting "lunch-and-learn" sessions with real AI outputs can help teams practice spotting errors like hallucinations or tone mismatches. Pairing traditional testers with behavior-focused reviewers ensures AI responses are accurate and dependable.
AI is here to handle tasks, not replace people. As Dmitry Reznik, Chief Product Officer at OwlityAI, puts it:
"Human expertise in quality assurance AI remains indispensable for critical decision-making."
The key to success lies in embracing AI as a tool while leveraging human creativity, judgment, and strategic thinking to deliver exceptional quality.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
The move from traditional QA to AI-driven testing isn’t about replacing roles - it’s about transforming them. Where traditional QA teams focused on manual testing, writing scripts, and analyzing requirements, AI Test Analysts are now tasked with selecting advanced tools, training machine learning models, and managing autonomous systems that evolve alongside application changes.
The data highlights this shift: 65% of QA professionals already incorporate AI into their workflows, with 43% seeing major gains in productivity and test coverage. AI-powered tools like self-healing and automated test generation can slash maintenance costs by 50% or more, while test execution becomes up to 10 times faster compared to older methods. For instance, Microsoft’s internal systems flagged 49,000 flaky tests, preventing around 160,000 false failures.
The workflows themselves tell a different story. Traditional QA often operated in isolated stages with batch testing cycles. AI-driven QA, on the other hand, integrates seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines, enabling real-time adjustments and pre-sprint test creation. Instead of spending hours fixing scripts after UI changes, AI systems now automatically update locators and adapt to evolving codebases, freeing analysts to focus on higher-value tasks.
The future lies in hybrid teams - where AI’s speed and efficiency complement human creativity and judgment. While AI takes care of repetitive regression testing and data-heavy tasks, human testers can focus on exploratory testing, business logic, and strategic quality planning. As Hannah Son from TestRail puts it: "AI isn’t replacing testers; it’s helping some work more efficiently. But for most, the shift is still just beginning."
For those ready to embrace this evolution, tools like Rock Smith make the transition easier. These platforms use AI agents to visually interpret applications and create test flows in plain English - no advanced coding required. The real question isn’t whether to adopt AI in QA, but how quickly your team can adapt to stay ahead in 2026 and beyond.
FAQs
What skills do I need to become an AI Test Analyst?
To step into the role of an AI Test Analyst, you'll need a blend of technical expertise, sharp analytical thinking, and the ability to work well with others. On the technical side, it's important to have a solid grasp of AI and machine learning concepts, along with experience in automation frameworks and scripting languages. Analytical skills play a big role too - whether it's crafting effective test cases or making sense of AI-driven insights. And let’s not forget communication: being able to collaborate with different teams ensures that testing stays aligned with the project’s objectives. A strong foundation in both AI literacy and testing know-how is key to thriving in this field.
When should a team keep manual testing instead of AI?
Manual testing remains important when human judgment, creativity, and intuition are required. It plays a key role in spotting unpredictable user behaviors, subtle usability problems, and intricate scenarios that AI tools might overlook. It's particularly useful during the early stages of development or when verifying AI-generated outcomes. This approach ensures accuracy in areas where AI might struggle, such as dynamic situations or unclear user interactions.
How do you trust and validate AI-generated tests?
To keep AI-generated tests reliable, a mix of human review and automated validation works best. Human testers can focus on reviewing essential test scripts, while methods like signed diffs and traces help confirm changes. Tools such as Rock Smith add another layer by visually interpreting applications, creating test flows in plain English, and enabling real-time execution. This combination helps reduce false positives and ensures the tests remain dependable.


