Local vs. Cloud Browser Testing for QA Teams
Compare local vs cloud browser testing for QA teams—costs, setup time, speed, device coverage, security, and when to use local, cloud, or hybrid.

Local vs. Cloud Browser Testing for QA Teams
QA teams face a key decision: manage tests on local machines or leverage cloud-based platforms. Here's a quick breakdown:
- Local Testing: Offers full control over browsers, operating systems, and updates. However, it’s costly, time-consuming to set up, and scales poorly. Running tests sequentially slows down larger test suites, and maintaining hardware adds ongoing expenses.
- Cloud Testing: Provides access to thousands of browser and device combinations, enables parallel testing, and reduces setup time. It’s cost-efficient and ideal for large-scale testing. But it requires a stable internet connection and involves third-party data handling.
Quick Comparison
| Aspect | Local Testing | Cloud Testing |
|---|---|---|
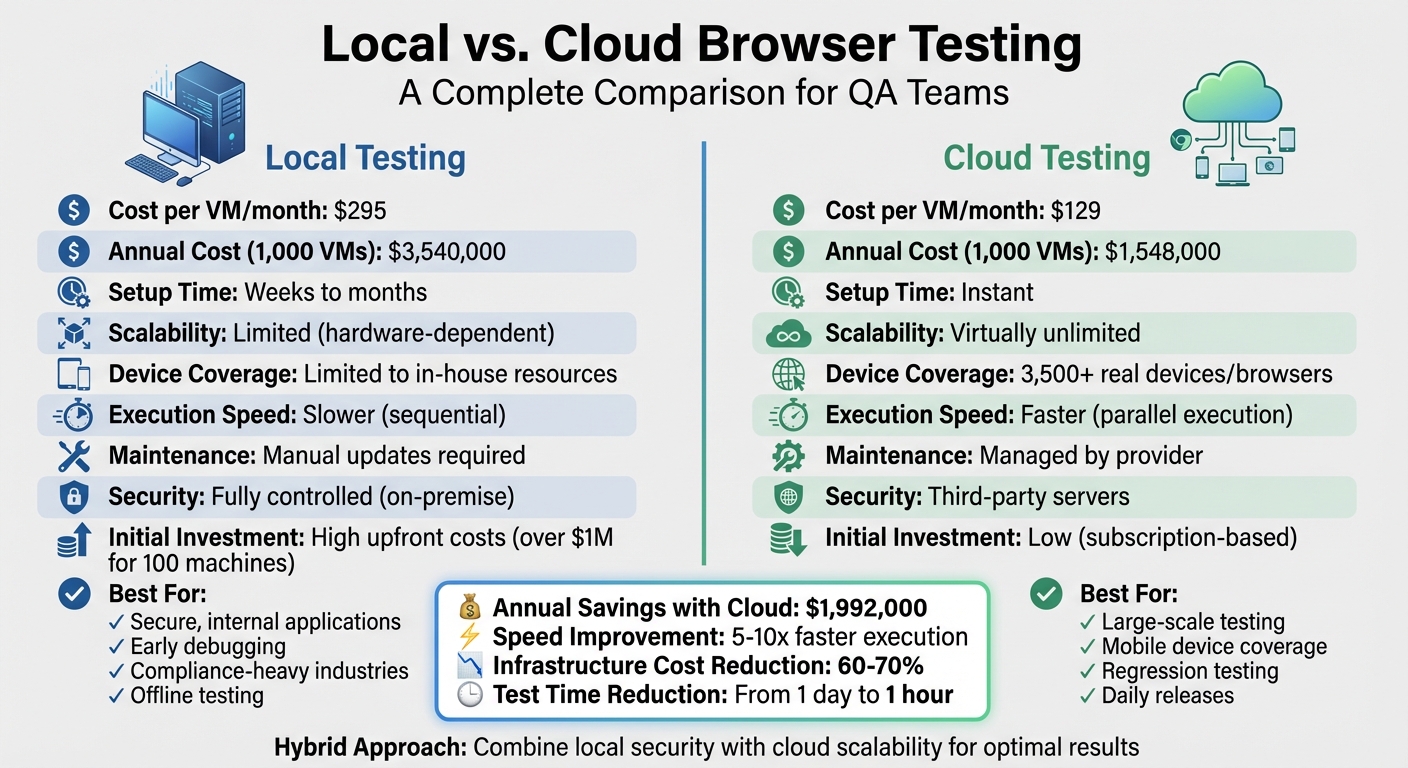
| Cost per VM/month | $295 | $129 |
| Setup Time | Weeks to months | Instant |
| Scalability | Limited (hardware-dependent) | Virtually unlimited |
| Maintenance | Manual updates and upkeep required | Managed by provider |
| Device Coverage | Limited to in-house resources | Access to 3,500+ real devices/browsers |
| Execution Speed | Slower for large test suites (sequential) | Faster (parallel execution) |
| Security | Fully controlled (on-premise) | Data stored on third-party servers |
Key Takeaway
Local testing is best for secure, internal applications or early debugging. Cloud testing excels in scalability, speed, and broad device coverage. For sensitive projects, a hybrid approach combines the strengths of both methods, offering flexibility and control.
Local vs Cloud Browser Testing: Cost, Speed, and Scalability Comparison
Setup and Infrastructure Requirements
Local Testing Setup
Setting up a local browser testing environment involves managing physical hardware and infrastructure. This includes securing devices, ensuring proper environmental conditions (like cooling and power), and allocating adequate space and storage. Your team will also need to install operating systems, multiple browser versions (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge), virtualization drivers, and browser binaries by hand. On top of that, every time a browser is updated, manual updates are required.
This process isn't quick - it can take anywhere from weeks to months to fully establish a testing environment. Along the way, you might face technical issues, such as compatibility problems with virtualization drivers or memory limits that hinder saving test screenshots. Beyond the setup, there’s the ongoing effort to keep everything updated. Real device labs require constant maintenance to stay compatible with the latest devices, operating systems, and browsers, making this approach both costly and time-intensive.
Cloud Testing Setup
Cloud-based environments simplify the entire process.
With cloud platforms, there’s no need for physical hardware. Instead, you access browser and device environments directly through your web browser - no installations necessary. For specific needs, like testing private servers or localhost environments, you might download a local binary (e.g., BrowserStack Local for Windows, macOS, or Linux) to establish a secure testing tunnel. This secure connection is easily set up using your access key.
Cloud providers take care of updates, scaling, and maintenance automatically. You gain immediate access to over 3,500 real device and browser combinations without the delays of hardware procurement or software setup. This means you can start testing right away, skipping the lengthy preparation process.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Local (In-House) Testing | Cloud-Based Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | High upfront costs for hardware and setup | Low upfront costs; subscription-based |
| Setup Time | Weeks or months | Instant; ready-to-use environments |
| Hardware Needs | Physical devices, servers, cooling, storage | None (managed by provider) |
| Software Management | Manual OS and browser binary installation | Minimal (browser access or local binary) |
| Maintenance | Manual updates, patching, hardware upkeep | Handled entirely by service provider |
| Cost per VM/Month | $295 (hardware, software, manpower) | $129 (subscription only) |
| Annual Cost (1,000 VMs) | $3,540,000 | $1,548,000 |
Up next, we’ll dive into the testing capabilities and coverage offered by these methods to further highlight their differences.
sbb-itb-eb865bc
Testing Capabilities and Coverage
Scalability and Coverage
Testing locally has its limitations, especially when it comes to hardware and software configurations. For instance, if you need to test Safari on macOS or Edge on Windows, you'll have to set up separate machines or virtual environments to cover those scenarios. Another drawback is that local tests run one after another, meaning the more tests you have, the longer it takes - execution time increases step by step. Add to that the fact that local setups can only scale so far, and it’s clear why these environments can fall short.
In contrast, cloud platforms completely change the game. They provide access to over 3,500 browser and OS combinations, including older versions and newer mobile devices. Plus, they allow tests to run in parallel, cutting down execution time dramatically - from a full day to just about an hour. This is especially important for mobile testing. Relying on local emulators can leave you blind to certain edge cases that only real devices reveal. And with around 83.72% of the global population using smartphones, testing on real devices isn’t just a luxury - it’s a necessity.
Here’s how one Delivery Manager described the impact of switching to a cloud solution:
"Before BrowserStack, it took eight test engineers a whole day to test. Now it takes an hour. We can release daily if we wanted to."
– Martin Schneider, Delivery Manager
This kind of efficiency is a game-changer for modern QA processes, where speed often determines success.
Hybrid Solutions for QA Teams
Sometimes, neither local nor cloud testing alone can meet every need. That’s where hybrid solutions come in. These approaches combine the security of local testing with the scalability of cloud platforms. For example, Rock Smith’s local browser execution (https://rocksmith.ai) allows tests to run within your own infrastructure, ensuring sensitive data stays protected behind your firewall. At the same time, it uses AI-driven test generation and semantic targeting to enhance test coverage. This makes it a great option for applications hosted on localhost or behind VPNs that can’t be exposed to public cloud environments.
Pros and Cons of Local and Cloud Browser Testing
Local Browser Testing: Pros and Cons
Local browser testing gives you complete control over your testing environment. Everything stays securely behind your company’s firewall, which is especially crucial for industries like healthcare and finance that have strict compliance requirements. Plus, debugging is faster since everything is under your direct management, allowing for quicker detection and resolution of issues.
However, this level of control comes with a hefty price tag. Setting up an in-house lab with 100 machines can cost over $1,000,000 upfront for hardware, networking, and facilities. On top of that, annual power consumption can exceed $50,000, and cooling adds another $30,000. And it’s not just about money - managing this infrastructure consumes a significant amount of time. Roughly 40% of QA time might be spent maintaining the setup instead of running actual tests.
Here’s a breakdown of the pros and cons:
| Feature | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Full control over updates and customization | Limited by the physical capacity of the hardware |
| Security | Data stays securely behind the firewall | High upfront costs (over $1M for 100 machines) |
| Debugging | Quick feedback for early bug detection | Sequential testing can slow CI/CD pipelines |
| Maintenance | No reliance on external providers | Requires a dedicated team for ongoing support |
| Coverage | Can operate offline without internet access | Limited to devices that are manually maintained |
Cloud Browser Testing: Pros and Cons
Cloud-based testing eliminates the need for costly infrastructure. Instead, you get on-demand access to thousands of browser and OS combinations, with tests running in parallel. This setup can make your test suite 5 to 10 times faster compared to local environments. Another big advantage is the shift in costs - from high upfront investments to predictable monthly fees. This change can reduce infrastructure expenses by 60% to 70%.
That said, cloud testing has its trade-offs. A stable internet connection is a must, and poor network conditions can lead to latency issues. Security is another concern since data is stored on third-party servers, raising risks like account hijacking or insecure APIs.
Here’s a closer look at the benefits and drawbacks:
| Feature | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Unlimited parallel execution | Requires a reliable internet connection |
| Cost | Cuts infrastructure expenses by 60–70% | Data is stored on external servers |
| Device Coverage | Access to 3,500+ to 9,000+ real devices | Latency can impact test execution |
| Maintenance | Updates and upkeep are handled by the provider | Less control over the testing environment |
| Speed | Reduces execution time from days to hours | – |
The financial difference between local and cloud solutions is striking. For a setup with 1,000 virtual machines, in-house testing costs about $3,540,000 annually, while cloud-based testing costs roughly $1,548,000 - a savings of nearly $2 million.
🚀 Modern QA Automation: Hybrid Local & Cloud Testing with Zalenium, Selenoid, and Cloud Platforms.✨💻
Performance, Cost, and Security Considerations
Let’s take a closer look at the practical aspects of performance, cost, and security that set local and cloud testing apart.
Execution Speed and Debugging
Local testing shines when it comes to immediate feedback, thanks to the absence of network delays. This makes it an excellent choice for quick debugging during development. However, this advantage fades when dealing with large test suites. For instance, running 10 tests sequentially on a single machine can take significantly more time compared to running just one.
On the other hand, cloud testing takes advantage of parallel execution across multiple virtual machines, drastically reducing the time needed for large test suites. Cloud platforms offer on-demand computational power in environments designed to minimize resource conflicts. Moreover, features like intelligent test selection can reduce test cycles by up to 50% by focusing only on tests impacted by recent code changes. These differences in performance can significantly impact the cost-efficiency of each approach.
| Feature | Local Browser Testing | Cloud Browser Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Execution Speed | Quick for single tests; slower for suites (sequential) | Slightly slower per test (due to network latency); fast for suites (parallel) |
| Scalability | Limited by local hardware (CPU/RAM) | Virtually limitless on-demand scaling |
| Debugging | Depends on local logs and screenshots | Includes videos, automated logs, and AI-driven insights |
| Maintenance | High (manual updates and patching required) | Minimal (managed by the cloud provider) |
Cost Analysis
When comparing costs, local setups come with hefty upfront expenses. Hardware, servers, and networking infrastructure require a significant initial investment, with ongoing costs like staffing adding approximately $55 per VM per month. In total, maintaining a local setup costs around $295 per VM per month, compared to $129 per VM per month for cloud solutions.
Cloud platforms, by contrast, operate on a subscription model, eliminating hardware upkeep and reducing the workload on internal teams. Beyond these savings, QA teams can avoid spending over $10,000 per tester on real device costs by opting for cloud-based testing.
Rock Smith offers flexible pricing designed to work with hybrid workflows. This means you can run tests locally for sensitive projects while scaling up in the cloud for broader coverage, without being locked into a rigid pricing structure.
Data Security and Compliance
While performance and cost are key factors, data security is often the deciding concern. Local testing provides complete control over sensitive data, keeping it within your infrastructure. This is especially important for industries like healthcare and finance, where regulatory compliance is critical.
Cloud testing, however, involves storing data on third-party servers, which can introduce potential risks. To mitigate these concerns, leading cloud providers use Secure WebSockets (WSS) and SSL over port 443 to encrypt data during transmission. They also ensure virtual machines are wiped clean after each session, removing browser history, cookies, cache, and form data. Additionally, top platforms comply with standards like SOC2 Type 2, GDPR, and CCPA.
Rock Smith's local browser execution is an excellent option for teams handling sensitive applications. By running tests entirely within your infrastructure, you maintain control over proprietary data while still benefiting from AI-driven testing capabilities. This approach combines the security of local testing with the advanced automation that modern QA teams need.
Best Use Cases for Local, Cloud, and Hybrid Testing
When to Choose Local Testing
Local testing is ideal for internal applications that aren’t publicly accessible yet - like those hosted on localhost, behind firewalls, or within proxy servers. It’s a go-to option during early development stages when the focus is on quickly catching bugs before sharing code with the team.
This method also serves as a safety net if your live product or cloud infrastructure goes offline. For smaller projects, where tests run one after another, local testing provides instant feedback. It’s particularly effective for unit tests and quick functional checks, often eliminating the need for a full cloud setup.
When to Choose Cloud Testing
For broader device and browser coverage, cloud testing is the way to go.
Cloud testing is indispensable when you need to validate your application across a wide range of devices and browsers - something that’s nearly impossible to replicate locally. It’s especially critical for mobile testing, where ensuring compatibility across various devices is a must.
One of the standout benefits of cloud testing is its ability to execute tests in parallel, drastically reducing testing time. What might take a full day locally can be completed in about an hour on the cloud, making daily releases achievable. It’s also perfect for regression testing of essential workflows - like login, checkout, and search - using AI-driven test selection to speed up cycles by as much as 50%.
Hybrid Approach with Rock Smith
When neither local nor cloud testing fully meets your needs, a hybrid approach can bridge the gap.
Rock Smith’s local browser execution brings together the security of local testing with the scalability and automation of cloud platforms. This hybrid strategy is particularly useful for QA teams working on sensitive applications that can’t risk exposure to external servers. It combines the best of both methods, offering flexibility, security, and control over proprietary data.
Conclusion
Deciding between local and cloud browser testing isn't about finding a "better" option - it’s about understanding how each fits into your testing strategy. Local testing provides complete control and secure data handling, making it ideal for early debugging and internal applications. On the other hand, cloud testing shines with its ability to run tests in parallel across thousands of real device-browser combinations. This efficiency can drastically cut test cycles, reducing them from a full day to just one hour.
Each approach comes with its own set of trade-offs. Local testing’s sequential execution can slow down larger test suites, while cloud testing depends on stable internet connections and third-party platforms. Industry experts advocate for a balanced approach. Judy Bossi from Functionize emphasizes this point:
"Local execution may promise faster initial feedback, but that feedback is unreliable if tests don't work. Eventually without testing in the cloud, your QA and Dev teams will get consumed by the test debt problem".
To overcome the limitations of relying solely on either method, a hybrid approach offers the best of both worlds. Rock Smith highlights how this strategy combines the security of on-premise testing with the scalability of cloud automation. With local browser execution, QA teams can safely test staging environments and internal applications without exposing sensitive data to external servers. Meanwhile, cloud features like AI-powered test flows, semantic targeting, and real-time monitoring enhance efficiency.
This hybrid model isn’t just a middle ground - it’s a smart, flexible solution. It provides instant feedback during development, ensures secure testing for private applications, and scales regression testing across real devices. For teams managing sensitive data or pre-release applications, this adaptability can make a critical difference.
FAQs
When should we choose local testing over cloud testing?
Local testing is a go-to option when you need quick, device-specific tests or a secure environment. By running tests directly on your machine, it’s perfect for rapid checks, internal app development, or situations demanding strict data privacy - like in healthcare settings.
The key advantage here is control and security. You have full oversight of the testing process, which is especially useful when working with sensitive data. However, there’s a trade-off. Local testing typically offers limited browser and operating system coverage, making it less effective for large-scale, cross-platform testing. For that, cloud-based solutions often prove to be a better fit.
How can we ensure cloud testing is secure and compliant?
When conducting cloud testing, it's crucial to prioritize security and compliance. Start by using encrypted protocols like HTTPS and WSS to safeguard data while it's being transmitted. Another key practice is regularly resetting test environments to a baseline state, which prevents unintended data persistence.
To further enhance security, implement measures such as security audits, strict access controls, and adherence to regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. These actions are essential for reducing risks and ensuring compliance in cloud-based testing scenarios.
What does a hybrid testing setup with Rock Smith look like?
A hybrid setup with Rock Smith offers the best of both worlds by combining local browser execution with cloud-based testing. On the local side, tests are securely executed on a developer's machine, making it a great choice for handling sensitive data or testing internal applications. Meanwhile, in the cloud, Rock Smith's AI-driven platform runs scalable and reliable tests across a variety of environments. This setup strikes a balance between security, speed, and scalability, creating a thorough and efficient QA process.