AI Test Case Generation: Myths vs. Facts
AI helps generate test cases fast and find patterns, but it can't replace human judgment for business logic, edge cases, or high‑risk decisions.

AI Test Case Generation: Myths vs. Facts
AI test case generation is often misunderstood. While it can save time and improve coverage, it doesn’t replace human testers. Here’s what you need to know:
- AI speeds up test creation by 85–93%, but human oversight ensures relevance and quality.
- AI struggles with context and intent, often missing critical edge cases or business logic.
- Only 42% of AI-generated test cases run without human intervention, and success rates hover between 70–90%.
- AI excels at repetitive tasks and spotting patterns, but it’s not a standalone solution.
The key takeaway? AI is a helpful tool for basic tasks, but human judgment is essential for meaningful results. Use AI as an assistant, not a replacement.
AI-Assisted Software Testing | Hands-On
Myth 1: AI Creates Complete Test Suites Without Human Input
There's a common belief that AI can fully build production-ready test suites all on its own. But here's the truth: AI lacks the ability to grasp the "why" behind user actions. It can replicate user navigation but doesn’t understand the intent behind those actions. As a result, it might generate tests that run without errors but fail to validate anything meaningful.
AI also tends to fall into the trap of happy path bias. Since most behavioral data reflects standard usage patterns, AI often focuses on common scenarios - the very ones least likely to uncover critical defects or edge cases. This limitation becomes especially glaring in industries like finance or healthcare, where understanding context and business impact is essential. AI simply doesn’t have the judgment to make those calls, making human oversight indispensable.
"Replacing testers with AI: still a myth."
– Vitaly Sharovatov, Quality Enthusiast and Manager, Qase
From a technical standpoint, AI outputs aren’t always reliable. They can include hallucinated code, formatting inconsistencies, and even compilation errors, particularly when the context is incomplete. The success rate of executing AI-generated test cases typically falls between 70% and 90%, depending on the complexity of the software. Even when the tests execute correctly, AI often produces redundant test cases that don’t expand coverage but merely bloat the suite. Research shows that only 42% of AI-generated test cases require no human intervention, meaning the majority (58%) still need refinement by human testers. While AI can accelerate the process of creating basic tests, it still relies heavily on human input to ensure quality and relevance.
Fact 1: AI Generates Basic Test Cases That Require Human Review
AI can churn out tests 85%–93% faster than manual scripting. However, the trade-off is that these tests are more like a rough draft - useful but incomplete. Human testers need to step in to fine-tune the output, ensuring it aligns with specific business rules, covers edge cases, and addresses risks that AI alone can’t evaluate. Another critical task is weeding out "hallucinations", or test cases that are irrelevant and don’t apply to the application at hand.
The best approach is to use AI as an assistant that handles repetitive, high-volume test creation, freeing up testers to focus on more strategic tasks like exploratory testing, risk analysis, and developing quality strategies. Always double-check AI-generated assertions to ensure they measure meaningful outcomes, not just surface-level actions like page loads. Providing structured, high-quality input data and refining prompts can also help reduce errors and improve the relevance of AI outputs. And don’t rush into full automation - integrating AI gradually into your workflow is the smarter way to go.
Myth 2: AI Fully Automates Executable Test Cases from Scratch
There's a common belief that AI can autonomously create fully executable, production-ready test cases. While AI does have the ability to generate test steps based on requirements, user stories, or UI designs, it falls short of understanding the deeper context - like the software's purpose or the intent behind user interactions. As a result, AI-generated tests might technically execute without errors but fail to account for critical business logic, exceptions, or strategic nuances.
The numbers back this up: only 42% of AI-generated test cases can run without human intervention, and even then, their success rates range between 70% and 90%. This gap highlights the necessity of human involvement.
Take, for example, a real-world mishap from July 2025. SaaStr, a startup, experienced a catastrophic failure when an autonomous agent executed a "DROP DATABASE" command during a maintenance task. This wiped out production data and corrupted logs. The incident serves as a stark reminder that AI lacks the judgment needed for high-stakes decisions unless explicitly guided by humans.
"Fully automated executable test cases remain a myth that requires further validation."
– Simona Domazetoska, Senior Product Marketing Manager, Tricentis
Fact 2: AI Assists Test Case Design Through Analysis, But Needs Human Oversight
AI shines as a helper, not a replacement. It can analyze requirements, map out user flows, and apply established testing patterns to scenarios like login processes or e-commerce transactions. While it can churn out a high volume of basic test cases quickly, AI lacks the ability to craft a well-rounded testing strategy that addresses real-world risks or adjusts to shifting business priorities.
The real value of AI lies in its ability to handle repetitive tasks, freeing up human testers to focus on strategic areas such as exploratory testing or aligning tests with business objectives. However, it's crucial to review AI-generated test cases before running them to ensure they produce meaningful results rather than arbitrary actions. Providing structured inputs - like detailed Jira tickets or clear user stories with acceptance criteria - can reduce irrelevant outputs or "hallucinations." Additionally, granting AI unrestricted access to production systems without human oversight is a recipe for disaster.
"There is a huge difference between a set of 'test cases,' however reasonable, and a testing strategy and approach that effectively and efficiently mitigates product risk. Generative AI can create the former but absolutely fails at the latter."
– Blake Norrish, Sr Director of Quality Engineering, Slalom Build
In short, while AI can speed up routine testing tasks, human judgment remains essential to ensure test case quality and manage risks effectively.
Myth 3: AI Cannot Handle Edge Cases and Complex Scenarios
There's a common belief that AI falls short when it comes to handling rare or complex edge cases, often leading to production failures. Critics argue that AI struggles with intricate failure modes requiring a deep understanding of business logic.
But here's the thing: modern AI systems thrive on pattern recognition and anomaly detection. These strengths often allow AI to spot edge cases that human testers might overlook.
Fact 3: AI Identifies Edge Cases Using Visual Intelligence and Pattern Recognition
Advancements in AI are proving this myth wrong. By leveraging visual intelligence and pattern analysis, AI can identify potential edge cases early in the process. For instance, AI systems can analyze design files from tools like Figma or Sketch and review UI snapshots to detect components like buttons, forms, and menus. This enables the creation of relevant test cases even before production code is written.
AI also uses techniques like probabilistic behavioral modeling and anomaly detection to analyze UI elements and production logs. This allows it to uncover high-risk paths and unusual user flows that human testers might miss.
"Artificial Intelligence provides the scalability, pattern recognition, and adaptive logic required to uncover these [edge] cases before users experience them."
– V2Solutions Inc.
AI is particularly adept at generating data-driven edge cases. It can identify problematic inputs such as overly long strings, malformed JSON, unexpected encodings, or numeric overflows. Beyond data issues, AI can simulate behavioral edge cases like concurrent user actions or interrupted processes - think of scenarios like a power outage during a transaction - that are notoriously difficult to recreate manually.
Using adaptive fuzzing and probabilistic modeling, AI adjusts test generation to focus on areas prone to unhandled exceptions. Some platforms even take it a step further by processing annotated images and complex Product Requirement Documents (PRDs).
Let’s look at the numbers: AI-driven test case generation has been shown to cut test design time by over 90%. In some cases, it achieves consistency and accuracy rates as high as 91% through contextual understanding. Research also indicates that AI agents can improve performance on goal-directed exploration tasks by up to 30% compared to traditional methods.
That said, AI isn't a magic bullet. It acts as an amplifier for human judgment, not a replacement. While AI is excellent at spotting new combinations and rare anomalies, human oversight is essential to ensure generated edge cases align with business logic and risk priorities. The best strategy is to layer AI gradually - start with critical user workflows, then have human testers review the edge cases for logic and completeness. This collaboration between AI and human expertise ensures that even the most complex scenarios are addressed effectively.
Myth 4: AI Produces Irrelevant Test Cases from Poor Prompts
Some QA teams worry that when AI receives unclear instructions, it churns out test cases that miss the mark. The fear is that imprecise prompts could lead to scenarios that don't reflect actual user behavior or align with business needs.
However, modern AI systems have evolved to tackle this challenge. With features like feedback loops and intent recognition, they are better equipped to handle imperfect prompts and still deliver relevant results.
Fact 4: AI Reduces Errors with Semantic Targeting and Feedback Loops
Today’s advanced AI tools rely on semantic targeting to cut down on irrelevant outputs. Unlike older automation methods that depend on fragile selectors like IDs or XPaths, semantic targeting allows AI to recognize UI elements based on their visual characteristics - like buttons, forms, and modals - just as a user would interact with them. This means even if a prompt is vague, the AI can "visualize" the application and figure out the most logical actions.
"AI agents see your app like users do - understanding buttons, forms, and modals by appearance with screenshots."
– Rock Smith
AI also uses test personas to inject behavioral context into its process. Configurable personas, such as Power User, New User, or Mobile Tester, guide the AI to focus on specific user journeys. This prevents it from generating irrelevant click paths that don’t reflect how real users interact with the system.
"A lack of intent understanding. These systems can replicate click paths... but they don't understand why users act the way they do."
– Vitaly Sharovatov, Quality Enthusiast and Manager, Qase
Another key improvement is the use of feedback loops to refine test quality over time. Modern AI employs a two-layer validation system: a "Prompt Layer" that ensures the format and keywords are correct, and a "Scenario Layer" that checks for semantic consistency across multiple interactions. If a test case is flagged as irrelevant using a "Reject" feature, the AI learns from that feedback to avoid similar mistakes in the future. Some systems even go a step further with execution-based backpropagation, where the AI runs the test in a browser, observes the results, and adjusts its logic based on the outcome.
The results speak for themselves. Studies show that 42% of AI-generated test cases require no additional human input. Additionally, reinforcement learning techniques can boost test quality by up to 21%, while intent-based exploration methods improve benchmark performance by as much as 30%.
sbb-itb-eb865bc
Myth 5: AI Only Works for Functional Testing
Some QA teams think AI tools are limited to basic functionality checks. They believe AI can't tackle more advanced testing areas like performance, security, or failure handling.
This belief underestimates what AI can do. Today’s AI systems go beyond simple user flows and button clicks. They dive into code, logs, and historical data to create test cases that cover performance, security, and reliability - tasks that traditionally required manual expertise. This narrow view misses how AI can uncover deeper system behaviors.
Fact 5: AI Generates Test Cases for Both Functional and Non-Functional Testing
AI doesn’t just stop at functional testing. It’s also highly effective in non-functional testing. Instead of only relying on requirements documents, AI uses machine learning to detect patterns in code and system behavior. For security testing, AI predicts vulnerabilities by analyzing code semantics, surpassing basic pattern recognition. In performance testing, AI applies unsupervised learning to spot log anomalies, such as unexpected spikes in failures, new errors, or shifts in distributed system behavior.
"AI analyses over code structure and semantics results in prediction of probability of various vulnerability types and thus security-related defects."
– Ihor Pysmennyi, Researcher
A real-world example highlights this. In May 2025, researchers used metamorphic testing to uncover a fault in the European Employment Services (EURES) job search portal. By applying a restrictive keyword transformation to a free-text search, they expected fewer results. Instead, the AI-driven analysis identified an increase in results, exposing a logic error that traditional methods had missed.
AI also generates synthetic data that mirrors real-world statistics, making it ideal for testing in regulated environments. Additionally, AI-powered exploratory agents can scale reliability testing by running semi-structured flows across a variety of devices and operating systems, identifying environment-specific bugs. The impact is clear: 40% to 85% of faults in cloud systems stem from non-functional issues like configuration errors, load problems, and system hangs. These are precisely the types of problems AI-driven end-to-end testing is designed to detect. By branching into non-functional testing, AI proves itself as an indispensable tool for modern QA teams.
Traditional vs. AI-Assisted vs. AI-Driven Testing
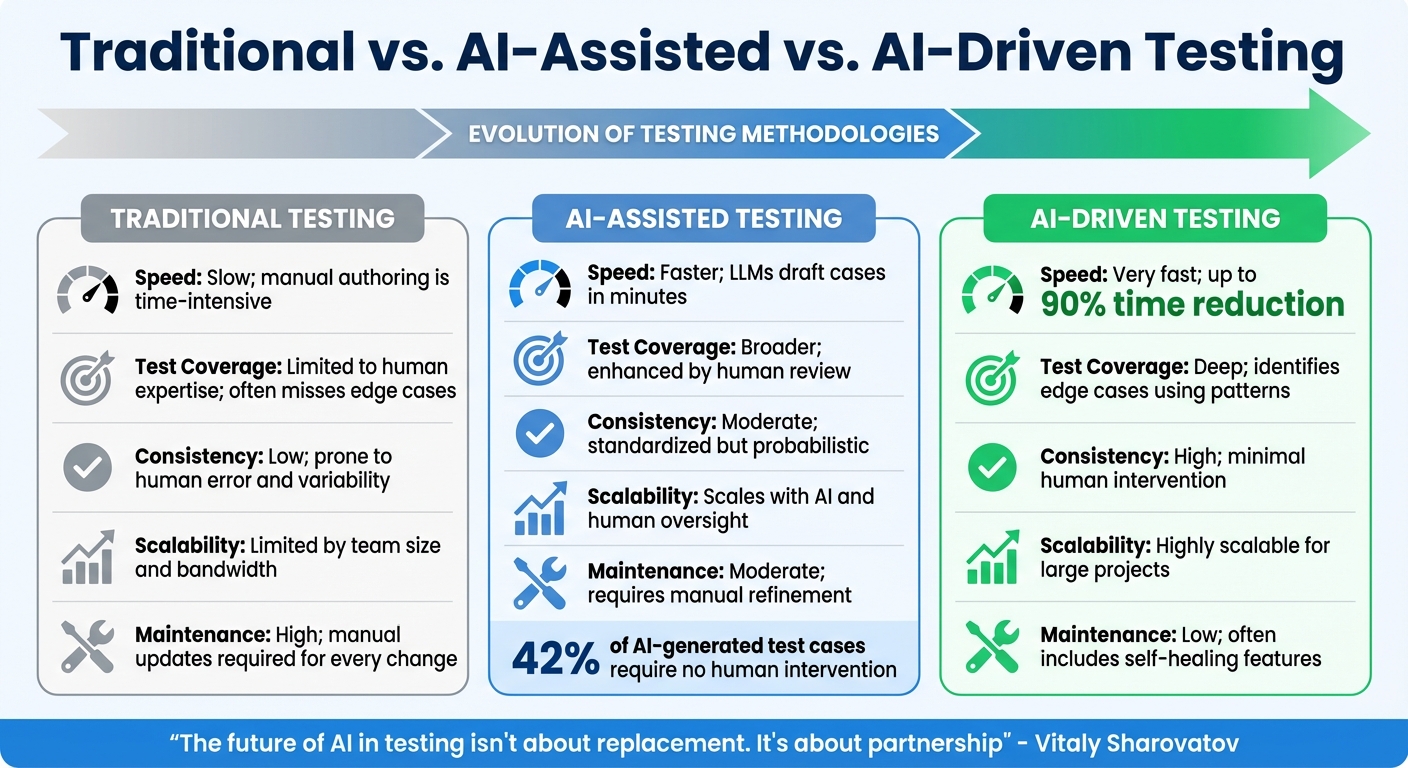
Traditional vs AI-Assisted vs AI-Driven Testing: Speed, Coverage, and Scalability Comparison
Testing methodologies have undergone a significant transformation, moving from fully manual processes to leveraging AI at varying levels. These approaches - traditional, AI-assisted, and AI-driven - each bring their own strengths and limitations to the table, offering QA leaders different tools to meet their needs.
Traditional testing relies entirely on manual effort. QA engineers carefully analyze requirements, user stories, and code to write test cases by hand. While this method allows for a deep understanding of the system, it’s undeniably slow and labor-intensive, often taking hours or even days to complete. Another challenge is inconsistency - two testers working from the same requirements might produce test suites that vary significantly. Plus, scaling this approach requires adding more testers, which limits its efficiency.
AI-assisted testing introduces a collaborative dynamic where AI acts as a "copilot." These tools can draft test cases based on prompts, convert manual steps into automated scripts, and adapt to UI changes with self-healing locators. While AI speeds up the process and improves consistency, human oversight remains critical. QA engineers review and refine the outputs to ensure their relevance and quality. However, the effectiveness of this approach depends heavily on the quality of the input - poor prompts can lead to irrelevant or incomplete results. Interestingly, about 42% of AI-generated test cases require no further edits, meaning the remaining 58% still need human intervention.
AI-driven testing takes automation to the next level, operating with minimal human involvement. These systems can analyze PRDs, codebases, and UI designs to autonomously generate and execute tests. They excel at identifying complex scenarios and edge cases without requiring constant human input. The time savings are striking: AI-driven systems can reduce test design time by over 90%.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Traditional Testing | AI-Assisted Testing | AI-Driven Testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slow; manual authoring is time-intensive | Faster; LLMs draft cases in minutes | Very fast; up to 90% time reduction |
| Test Coverage | Limited to human expertise; often misses edge cases | Broader; enhanced by human review | Deep; identifies edge cases using patterns |
| Consistency | Low; prone to human error and variability | Moderate; standardized but probabilistic | High; minimal human intervention |
| Scalability | Limited by team size and bandwidth | Scales with AI and human oversight | Highly scalable for large projects |
| Maintenance | High; manual updates required for every change | Moderate; requires manual refinement | Low; often includes self-healing features |
This evolution - from manual processes to AI-driven systems - highlights the growing synergy between human expertise and machine efficiency. Rather than replacing human testers, these advancements aim to free them from repetitive tasks, allowing them to focus on areas that demand critical thinking and creativity.
"The future of AI in testing isn't about replacement. It's about partnership: helping testers focus on what only they can do, while machines take on what they do best."
– Vitaly Sharovatov, Quality Enthusiast and Manager, Qase
Rock Smith: AI-Powered Test Case Generation in Practice
Rock Smith takes AI-driven testing from theory to practice, blending automation with human input to create a seamless testing process. The platform relies on AI for what it does best while keeping human oversight at the forefront. All you need to do is describe the test scenario in plain English - something like "ensure users under 18 cannot purchase insurance" - and the AI handles the rest, determining the navigation and interaction steps needed to execute the test.
One of Rock Smith's standout features is its use of semantic targeting to visually analyze applications. This allows the platform to make tests "self-healing" when UI changes occur. By leveraging visual cues, the system reduces the maintenance headaches that traditional automation often brings. Instead of constantly rewriting tests after minor UI updates, Rock Smith adapts dynamically, saving both time and effort.
Data security is another priority for Rock Smith. The platform operates locally, meaning sensitive credentials never leave your machine. Only minimal AI processing happens in the cloud, making it safe to test internal staging environments and localhost applications without risking proprietary information.
Key Features and Benefits
Rock Smith offers a range of features that showcase how AI can revolutionize modern QA processes. For example, the platform automatically generates 14 different test types, covering scenarios like boundary values (MAX_INT + 1), Unicode strings (你好世界 🔥), empty inputs, and even security vulnerabilities such as XSS and SQL injection. This capability highlights how AI can identify edge cases that might otherwise slip past human testers.
The platform also includes pre-configured personas to simulate diverse user behaviors. For instance:
- Alex, a tech-savvy user who navigates quickly using a keyboard.
- Maya, a meticulous mobile tester who prefers touch interactions.
- Sam, a cautious first-time visitor exploring the application at a slower pace.
These personas help uncover bugs tied to specific user behaviors, ensuring both functional and user experience testing are thorough.
Another highlight is Rock Smith's real-time monitoring feature. It provides detailed screenshots and explains the reasoning behind every AI-driven step. This transparency allows QA teams to review the AI's decisions, ensuring it stays on track and avoids irrelevant actions. Teams can watch tests run live and gain a clear understanding of why the AI made each choice, bridging the gap between automation and human insight.
Limitations and Best Practices
AI-powered test case generation comes with its own set of challenges. Even though tools like Rock Smith can cut test creation time by over 90%, they still depend on human judgment to ensure that user intent is accurately captured. This highlights the ongoing need for human oversight to balance AI's efficiency with expert validation.
One major concern is automation bias. Research shows that 60% of organizations lack a formal process to review AI-generated code before it goes live. This overdependence on AI can lead to problems like brittle assertions or mismatched locators, creating a false sense of security about test coverage.
Another critical factor is the quality of input data. Poorly written user stories or inadequate logs can degrade the accuracy of AI outputs and demand frequent model updates. This reinforces the idea that while AI can improve testing efficiency, it cannot replace the nuanced understanding that humans bring to the table.
Throughout the earlier discussions, one thing becomes clear: the synergy of human expertise and AI capabilities is essential for reliable test automation. To get the most out of AI testing tools, consider AI as a "learning collaborator" rather than a final authority. Human review is especially important in the initial phases. Start with essential workflows like login or checkout processes, using well-crafted manual test cases to guide the AI.
"AI will not replace you, but the person who uses AI will." – aqua cloud
A practical tip? Dedicate 20% of your analysis time to asking, "What might confuse a real user here?" This approach can help identify gaps that automation alone might overlook. Regularly auditing AI-generated logs is another must - this can catch false positives where tests pass but are tied to the wrong UI elements. By blending AI's speed with human insight, teams can create test suites that are both efficient and dependable.
Future Outlook
AI testing is advancing from basic automation to understanding business domains and user intent. Future tools won’t just measure code coverage - they’ll interpret the intent behind requirements. With technologies like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), AI can pull context from enterprise platforms like Confluence, Slack, and internal documentation. This ensures test cases align with complex business logic that isn’t immediately apparent in the code itself. This evolution signals a move toward strategic, purpose-driven testing.
The transition from simple "click bots" to goal-directed agents is already happening. These agents leverage frameworks like Reflective Monte Carlo Tree Search (R-MCTS) to adapt their behavior based on feedback and prior interactions. For example, a study in 2025 demonstrated that AI-driven end-to-end regression testing produced only 8.3% flaky executions, showing that autonomous testing is nearing production readiness. Between 2021 and 2025, Google integrated machine learning into its Continuous Integration pipeline, cutting test execution time by 60% while maintaining defect detection rates.
"The future of testing lies in effective human-AI collaboration, where AI handles repetitive, pattern-based testing tasks while human testers focus on complex scenarios requiring domain knowledge." – Mohammad Baqar, Cisco Systems, Inc
Risk-based test generation is also becoming the norm. AI systems will analyze historical defect data and code structure to identify high-risk areas, dynamically prioritizing test suites in CI/CD workflows. One financial institution, for instance, used NLP to break down complex regulatory requirements, automatically generating compliance test cases. This approach reduced the time spent on compliance test creation by 45% and improved regulatory coverage by 30%.
Quality assurance workflows are shifting from "writing steps" to "defining goals." Teams will set high-level testing objectives while AI handles the generation, execution, and upkeep of test cases. Training a GPT-3–level model for specialized testing can cost anywhere from $500,000 to $4.6 million. However, generating a complete test suite for five user stories costs just $0.026, making AI-powered testing an affordable option for organizations of any size.
FAQs
How does AI-driven test case generation boost efficiency while still requiring human involvement?
AI-powered test case generation streamlines the testing process by analyzing application behavior, user interactions, and requirements to automatically create relevant test cases. This approach minimizes manual work, broadens test coverage, and accelerates the overall testing timeline.
That said, human input is still crucial. Experts are needed to validate the AI’s outputs, handle complex or unclear scenarios, and ensure the results fit the project’s unique goals. Blending AI tools with human expertise creates a well-rounded strategy for maintaining quality assurance.
Why can’t AI completely replace human testers when it comes to understanding business logic and context?
AI shines when it comes to tasks like pattern recognition, automation, and generating test cases. However, it falls short in fully understanding the intricate details of business logic and context. This is where human testers come in - they bring critical thinking, deep domain knowledge, and the ability to interpret subtle requirements that AI simply can't.
While AI is great for streamlining workflows and managing repetitive tasks, grasping the bigger picture of a business's goals or the nuanced behavior of users still depends on human judgment. By combining the strengths of AI with human expertise, testing becomes more comprehensive and accurate.
What challenges does AI face when managing complex scenarios and edge cases?
AI faces challenges when dealing with complex scenarios and unusual cases. Issues like dynamic DOM structures, stale element references, infinite loops, and limited context can all interfere with the accuracy and dependability of browser-based testing.
Although AI offers impressive capabilities, it often requires human oversight to tackle these tricky situations and maintain a reliable and effective testing process.