Ultimate Guide to AI Test Maintenance Automation
How AI reduces test maintenance with self-healing locators, semantic targeting, and automated root-cause analysis to improve reliability and cut costs.

Ultimate Guide to AI Test Maintenance Automation
AI-powered test maintenance is transforming how QA teams handle automation challenges. Here's the core takeaway: AI reduces the time spent fixing broken tests by up to 95%, improves test reliability to 95–98%, and slashes maintenance costs. Traditional automation often consumes 60–80% of QA resources on maintenance, with fragile scripts causing frequent failures. AI addresses this by using self-healing locators, semantic targeting, and automated root cause analysis to handle changes without manual intervention.
Key Insights:
- Self-Healing Locators: Automatically updates broken test scripts by analyzing UI changes.
- Semantic Targeting: Understands element functions (e.g., "Click Submit") instead of relying on fragile identifiers.
- Automated Root Cause Analysis: Pinpoints whether failures are due to bugs or minor UI changes.
- Impact: Reduces manual maintenance by 70–95%, saving teams millions annually in labor and delays.
Why It Matters:
- Traditional testing methods lead to abandoned projects (68% fail within 18 months).
- AI boosts efficiency, cutting maintenance time from 60–80% to under 10% of QA effort.
- Companies see up to 400% increases in test coverage and faster releases.
AI isn't just about saving time - it's about making QA teams more effective and enabling quicker, more reliable software delivery. Let’s dive into how these tools work and how they can help you.
Can AI Maintain Test Automation without You
Problems with Traditional Test Maintenance
Traditional test maintenance is a resource-heavy process that can overwhelm even the most experienced QA teams. At the heart of the issue are fragile locators - CSS selectors, XPaths, and element IDs that are prone to breaking whenever developers rename a class or adjust the DOM structure. Something as simple as a button redesign can ripple through dozens of test scripts, forcing teams to manually identify and fix each failure.
These fragile locators significantly drive up maintenance costs. Here's the reality: maintenance eats up 60% to 80% of the total effort in test automation, leaving little room for testing new features. For every hour spent creating a test, teams often spend three hours repairing it. Take, for example, a UK-based specialty insurance marketplace. With 120 QA professionals, they dedicated over 120 days per release cycle solely to test maintenance - leaving no bandwidth for execution or expanding test coverage. Similarly, a global financial services company managing over 2,000 automated tests found that maintenance consumed 81% of their automation team's capacity, leaving a mere 19% for creating new tests.
"Maintenance will consume 60 to 80% of your automation effort. For every hour spent building tests, you'll spend three fixing them. The promise of 'automate once, run forever' becomes 'automate once, maintain constantly.'"
– Adwitiya Pandey, Senior Test Evangelist, Virtuoso QA
The bigger challenge isn't just repairing broken locators - it's the time spent investigating failures. QA engineers must dig into each issue, figure out whether it's a bug or a script problem, and ensure the fix works. This process creates a bottleneck, as only senior engineers typically have the expertise to handle these complexities. When these key team members leave, their knowledge leaves with them, further complicating the situation. Unsurprisingly, 68% of automation initiatives are abandoned within 18 months because the maintenance workload becomes unmanageable.
The fast pace of Agile and DevOps cycles makes things worse. Teams often find themselves trapped in "maintenance theater", where they spend more time fixing outdated tests than creating new ones. As false positives accumulate, trust in the CI/CD pipeline erodes, and developers start ignoring it altogether. For mid-sized enterprises, the financial impact is staggering - about $3.5 million annually on test maintenance, with delays adding up to $1 million per release.
Next up, we’ll look at how AI-driven solutions can tackle these problems head-on.
AI Techniques That Automate Test Maintenance
AI-powered test automation brings forward three advanced techniques designed to minimize script fragility and cut down on manual intervention. Let’s take a closer look at these methods and how they transform test maintenance.
Self-Healing Locators
Instead of relying on a single, fragile identifier for UI elements, AI uses a "fingerprint" approach. This involves analyzing multiple attributes like tag types, text, CSS classes, ARIA labels, DOM hierarchy, and relative positioning. When a locator breaks, the AI engine compares the current UI to historical snapshots to identify the correct element and automatically updates the locator in the test script - no developer input required.
This self-healing approach can reduce test failures by as much as 90%. Some advanced AI engines boast 99.97% element accuracy and have cut test flakiness by 80%. Companies using deep-learning–based self-healing report up to an 85% reduction in manual maintenance tasks.
"Self-healing test automation addresses this problem, it uses AI-driven models to detect UI, DOM or behavior changes and adapt tests automatically. Instead of failing on the first broken locator, the system recalibrates its understanding of each element and maintains the flow without human intervention."
– Tamas Cser, Founder & CTO at Functionize
Building on this, semantic targeting takes locator strategies to the next level.
Semantic Targeting
Semantic targeting shifts the focus from an element's fixed location to its intended function. Using natural language processing (NLP), AI can interpret plain instructions like "Click Submit" to identify elements by their purpose and context rather than their technical properties. For instance, even if a button's label changes from "ADD TO CART" to "ADD TO BAG", the system recognizes its function and adapts accordingly.
This contextual understanding helps avoid failures caused by minor property changes. Semantic targeting can reduce automated test failures by up to 90%, making it a game-changer for maintaining stability in dynamic UIs.
Automated Root Cause Analysis
This technique simplifies failure diagnosis by using AI to determine whether a test failure stems from an application bug or a minor UI change. Machine learning models analyze historical test data, logs, and recent code changes to identify high-risk areas. They also generate detailed reports with impact analysis and severity levels.
Studies by MIT CSAIL show that AI-driven defect prediction can achieve 87% accuracy, and organizations using these tools report a 35% boost in test coverage. By pinpointing specific code changes responsible for failures, this method has been shown to reduce build failures by up to 40%.
"Generative AI enables smarter, self-healing tests, adapting to changes and reducing the maintenance burden, paving the way for more resilient automation."
– ACL Digital
How Rock Smith Automates Test Maintenance
Rock Smith integrates advanced AI capabilities into a platform tailored for fast-paced engineering teams. Its approach tackles the challenges of brittle test scripts and the high costs of maintenance. By allowing tests to be described in plain English, the AI takes care of the technical details. Using visual intelligence and semantic targeting, the platform interprets applications much like a real user would. Let’s dive into how Rock Smith's features - visual intelligence, edge case generation, and real-time execution - streamline test maintenance.
Visual Intelligence and Semantic Targeting
Instead of relying on fragile CSS selectors or XPaths, Rock Smith’s AI analyzes application screenshots. For instance, if you instruct it to "Click the Submit button", the system identifies the element based on its appearance and context, not a technical identifier that could break after a code update. This visually driven, human-like approach allows tests to self-heal automatically when the user interface changes.
Edge Case Generation and Test Personas
Rock Smith doesn’t just focus on straightforward, happy-path testing. It automatically generates 14 different test types to catch edge cases often missed during manual QA. These include boundary value tests (e.g., MAX_INT + 1), security scenarios like XSS attacks (<script>alert(1)</script>) and SQL injection ('; DROP TABLE--), and tests involving complex Unicode inputs. To broaden coverage, the platform uses test personas that mimic diverse user behaviors. For example, tests can run under profiles like "Alex", a power user; "Maya", a mobile tester; or "Sam", a new user. This ensures thorough testing without duplicating logic.
Real-Time Execution and Local Browser Testing
Rock Smith runs tests directly on your local machine through a desktop application, ensuring sensitive data remains on-premises while only sharing test instructions. This setup works seamlessly with internal applications, staging environments, and localhost development. As tests execute, you receive live, step-by-step screenshots paired with AI-generated insights, helping distinguish real bugs from minor UI changes.
sbb-itb-eb865bc
Best Practices for AI-Powered Test Maintenance
Bringing AI into QA isn't just about flipping a switch. A significant chunk of test automation resources goes into maintenance, so having smarter strategies is crucial. Start by taking a hard look at your existing test suite to pinpoint "maintenance hotspots" - those tests that frequently break or demand excessive manual effort. This kind of audit helps you figure out where AI can make the biggest difference. From there, you can use these strategies to streamline maintenance even further.
Reusable and Modular Test Design
Think modular. By breaking down tests into smaller, reusable chunks - like login or navigation sequences - you can make updates in one place and have them apply across multiple scripts. A great tool for this is the Page Object Model (POM), which organizes UI elements into reusable objects. That way, when something changes, you only need to update one file. Keeping tests focused and under 50 steps also makes debugging a whole lot easier. And here’s a tip: name your methods based on business actions (like applyCoupon or proceedToPayment) instead of low-level steps. This makes your scripts more resilient when UI changes occur.
Smart Test Execution Strategies
Ditch those generic sleep() commands - they’re a recipe for flaky tests. Instead, use conditional waits that trigger based on events like element visibility. This keeps your tests in sync with the application. Integrating AI tools into your CI/CD pipeline (think Jenkins or Azure DevOps) allows for real-time execution and feedback, making your workflow much more efficient. Running tests in isolated environments minimizes outside interference, and regularly pruning outdated scripts ensures your suite stays streamlined and relevant.
Migrating Legacy Test Suites
Modernizing old tests is another big piece of the puzzle. Don’t just toss out your legacy suite all at once. Marsh McLennan, for example, piloted an AI-native testing platform and managed to cut maintenance time by 81%, saving $2.1 million annually. They started small, focusing on high-impact, high-maintenance areas - like core business workflows - before scaling up. During this transition, running legacy tests alongside AI-native ones ensures accuracy and builds trust before retiring the older tests.
Set clear thresholds for self-healing actions, like auto-approving small locator updates while flagging major workflow changes for human review. As Andy Dickin, Enterprise Account Director at Virtuoso QA, puts it:
"The 85% solution isn't a compromise; it's a revolution... When maintenance burden drops from 70% of QA effort to less than 10%, the entire economics of test automation changes."
This shift also allows traditional testers to take on more strategic roles. Instead of just running scripts, they can focus on high-risk areas and validate AI-generated scenarios. Companies using AI-native platforms report a 10× speed advantage in creating tests compared to older frameworks. That’s a game-changer for any QA team. This shift is driven by AI that tests like a human engineer, focusing on the user's perspective rather than just code.
Measuring Success and ROI of AI Test Maintenance
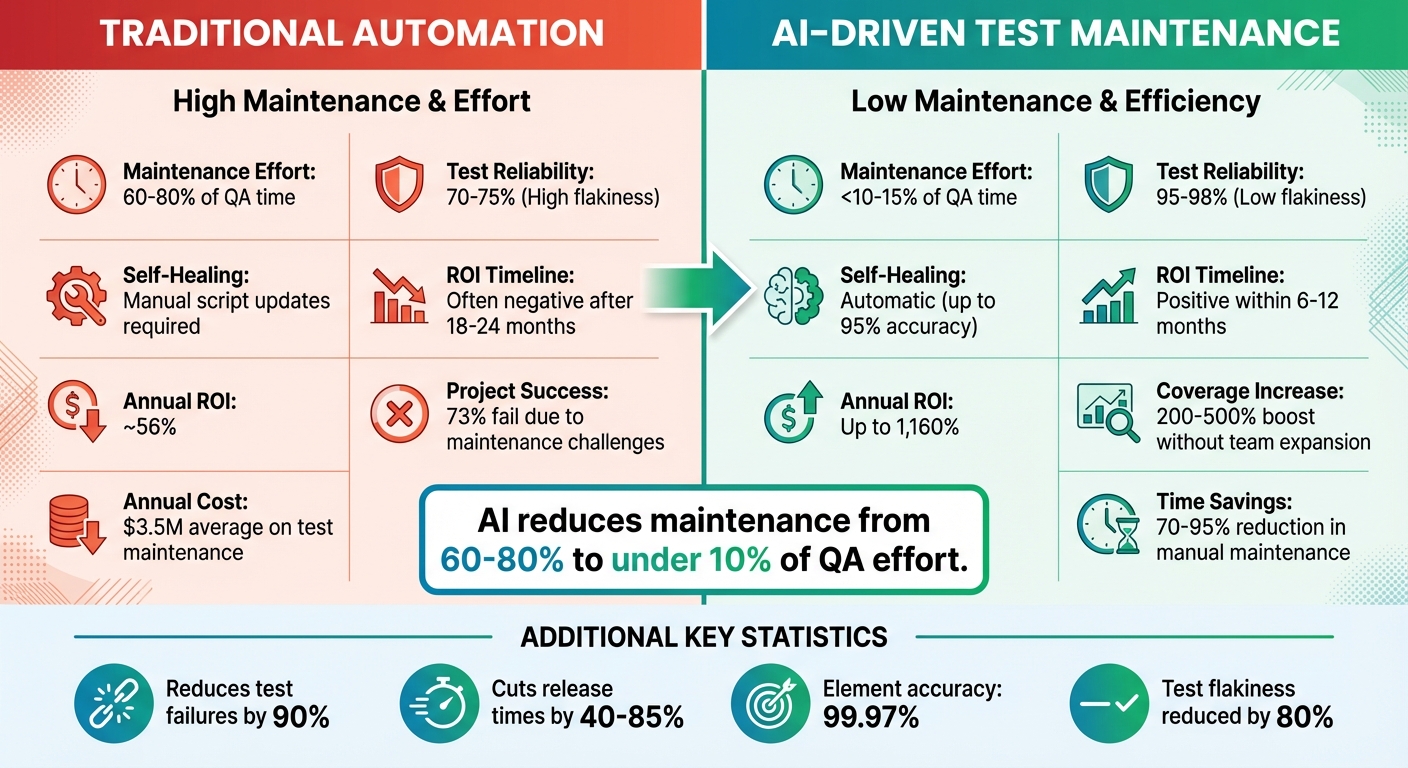
Traditional vs AI-Powered Test Maintenance: Key Metrics Comparison
Before diving into AI test maintenance, it’s crucial to evaluate where you stand. Start by auditing your current testing setup. Track metrics like hours spent fixing broken tests, test reliability percentages, and delays in releases. These benchmarks give you a clear picture of your starting point and help demonstrate the impact of AI to stakeholders with before-and-after comparisons. This groundwork highlights how AI can ease the burden of test maintenance.
Key Metrics to Track
A major area to monitor is the percentage of QA time spent on test maintenance. Traditional methods can consume 60–80% of QA effort, but AI-driven solutions slash this to under 10%. Test reliability is another critical metric - aim for 95–98% reliability compared to the 70–75% often seen with older methods. Additionally, keep an eye on mean time to repair (MTTR) for failing tests and the success rates of self-healing tools, with top AI systems achieving up to 95% accuracy.
Organizations adopting AI often see a 200–500% boost in test coverage without increasing team size. Release velocity is equally important, with AI cutting release times by 40–85%. These metrics provide a solid foundation for measuring the shift from traditional methods to AI-powered testing.
Traditional vs. AI Test Maintenance Comparison
The contrast between conventional and AI-driven approaches is striking. Companies relying on traditional methods spend an average of $3.5 million annually on test maintenance, with 73% of automation projects failing due to maintenance challenges. Here’s how the two approaches stack up:
| Metric | Traditional Automation | AI-Driven Test Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance Effort | 60%–80% of QA time | <10%–15% of QA time |
| Test Reliability | 70%–75% (High flakiness) | 95%–98% (Low flakiness) |
| Self-Healing | Manual script updates required | Automatic (up to 95% accuracy) |
| ROI Timeline | Often negative after 18–24 months | Positive within 6–12 months |
| Annual ROI | ~56% | Up to 1,160% |
For example, a telecommunications company reduced its regression testing cycle from ten days to three using AI-powered tools, which contributed to a 13% increase in sales. Similarly, a fitness brand cut maintenance time by 78%, saving approximately 130 hours each month.
Calculating ROI
To calculate ROI, use the formula: ROI = (Total Benefits - Total Costs) / Total Costs. Benefits typically include labor savings, faster time-to-market revenue, and reduced production defects. Costs cover software licenses ($30,000–$100,000 annually), infrastructure setup ($10,000–$30,000), CI/CD integration ($15,000–$25,000), and team training ($5,000–$10,000). ROI timelines vary: startups often see returns in 6–10 months, larger enterprises in 12–14 months, and mid-sized companies can achieve positive ROI in just six months.
One global financial services firm with 200 QA engineers spent 70% of their time on maintenance, costing $14 million annually. After implementing AI-driven maintenance, they reduced effort by 85% within 18 months, saving $11.9 million annually and increasing test coverage by 400%.
"The real ROI of AI-native testing isn't just cost savings. It's competitive velocity."
- Rishabh Kumar, Marketing Lead at Virtuoso QA
Beyond cost savings, the speed at which features are shipped can significantly impact revenue. Faster, more reliable testing through AI-powered maintenance isn’t just an operational improvement - it becomes a strategic advantage in staying competitive.
Conclusion
AI-powered test maintenance is reshaping QA workflows by tackling the long-standing issues of brittle scripts and high maintenance costs. Instead of spending 60–70% of their time fixing broken tests, teams can now focus on expanding test coverage and testing new features. This shift from reactive repairs to proactive optimization allows tests to self-heal when UI changes occur, cutting maintenance efforts by 70%.
The results? More reliable tests, shorter release cycles, and broader coverage - all without the need to onboard additional engineers. Companies adopting AI-driven maintenance report saving millions annually while accelerating their feature releases.
"AI transforms QA from a bottleneck into an accelerator."
- Eugenio Scafati, CEO, Autonoma
This evolution positions Rock Smith as a game-changer in modern QA workflows. Rock Smith’s advanced AI mimics how real users interact with applications, eliminating the headaches of brittle selectors and constant maintenance. Its semantic targeting adjusts automatically to UI changes, while local browser execution ensures sensitive data stays secure. With features like edge case generation spanning 14 test types and test personas that simulate diverse user behaviors, Rock Smith delivers comprehensive coverage without the usual upkeep.
Say goodbye to flaky tests and reclaim your team’s time. Try Rock Smith’s Pay-As-You-Go plan for just $0.10 per credit and see how AI-powered testing can transform your critical workflows.
FAQs
How does AI help reduce test maintenance time by up to 95%?
AI simplifies test maintenance by automating repetitive tasks and responding to application changes. Instead of depending on fragile, locator-based assertions, AI leverages visual validation to spot layout changes, missing elements, and text overlaps. This reduces the need for manual updates as user interfaces evolve, saving both time and effort.
Key AI-driven features, such as self-healing tests and automated test generation, enable tests to adapt dynamically to UI modifications without requiring heavy manual adjustments. Tools like Rock Smith take this a step further by employing AI agents to visually interpret applications, build test flows, and mimic real user behaviors. This approach not only streamlines test creation but also slashes maintenance time - by up to 95% in some cases.
What are self-healing locators in test automation?
Self-healing locators are AI-powered tools designed to make automated testing more resilient by automatically fixing broken element locators when a user interface (UI) changes. In traditional test automation, locators like XPaths or CSS selectors often break after UI updates, causing test failures. Self-healing locators tackle this issue by using AI to detect failures, pinpoint the correct elements, and dynamically update the locators - keeping tests stable without requiring manual fixes.
These locators operate by leveraging a mix of detection techniques, including IDs, CSS selectors, visual cues, and relative positioning. If a locator stops working, the system taps into historical data and alternative methods to accurately identify the element. This approach minimizes test flakiness, reduces false positives, and cuts down on maintenance time, making automated testing smoother and more dependable.
How does AI-driven test maintenance make release cycles faster and more efficient?
AI-driven test maintenance simplifies release cycles by automating how test cases are updated and managed. Traditional test automation often hits roadblocks with fragile tests that fail due to UI updates or dynamic content. These failures usually result in delays and require manual fixes. In contrast, AI-powered tools tackle this problem using methods like self-healing tests, visual AI, and semantic targeting. These techniques enable tests to adapt automatically to changes, cutting down on false positives and reducing the need for manual adjustments.
By keeping tests stable and dependable, teams benefit from quicker feedback loops and can concentrate on rolling out new features instead of constantly repairing broken tests. The result? Shorter release cycles, greater flexibility, and consistently better software quality.